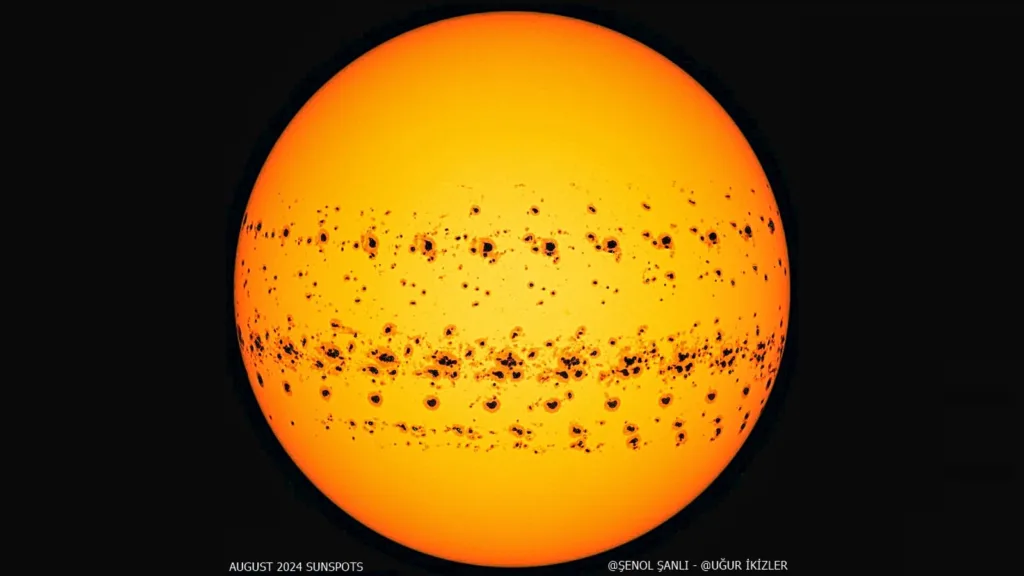
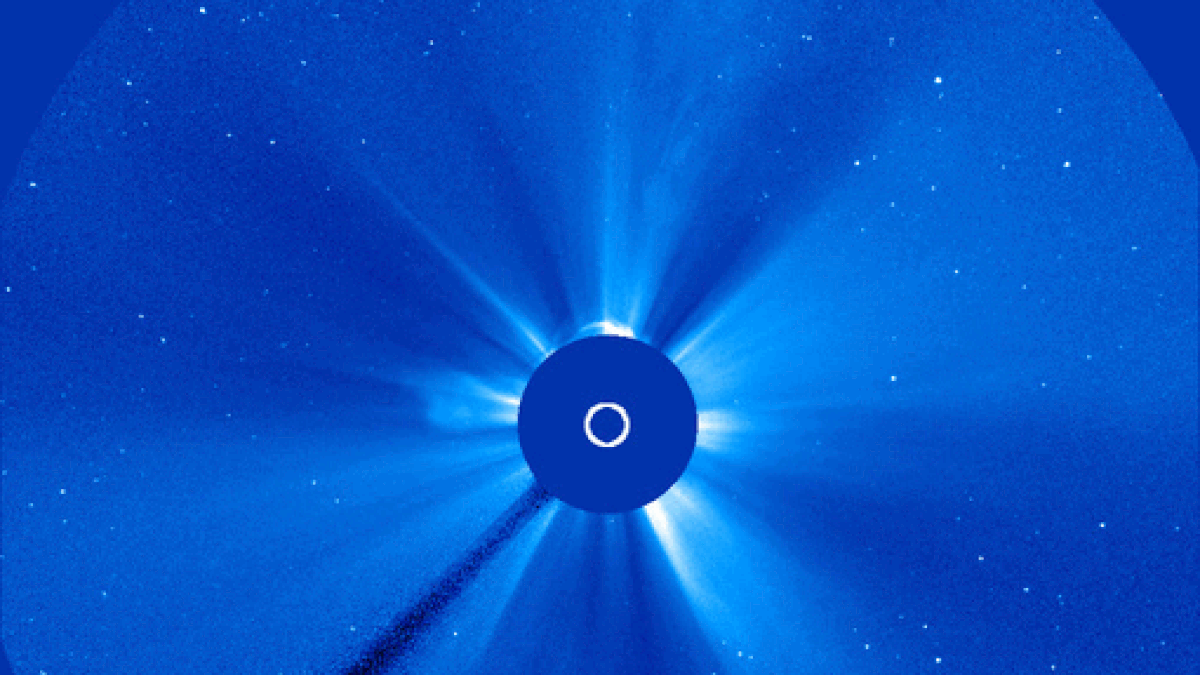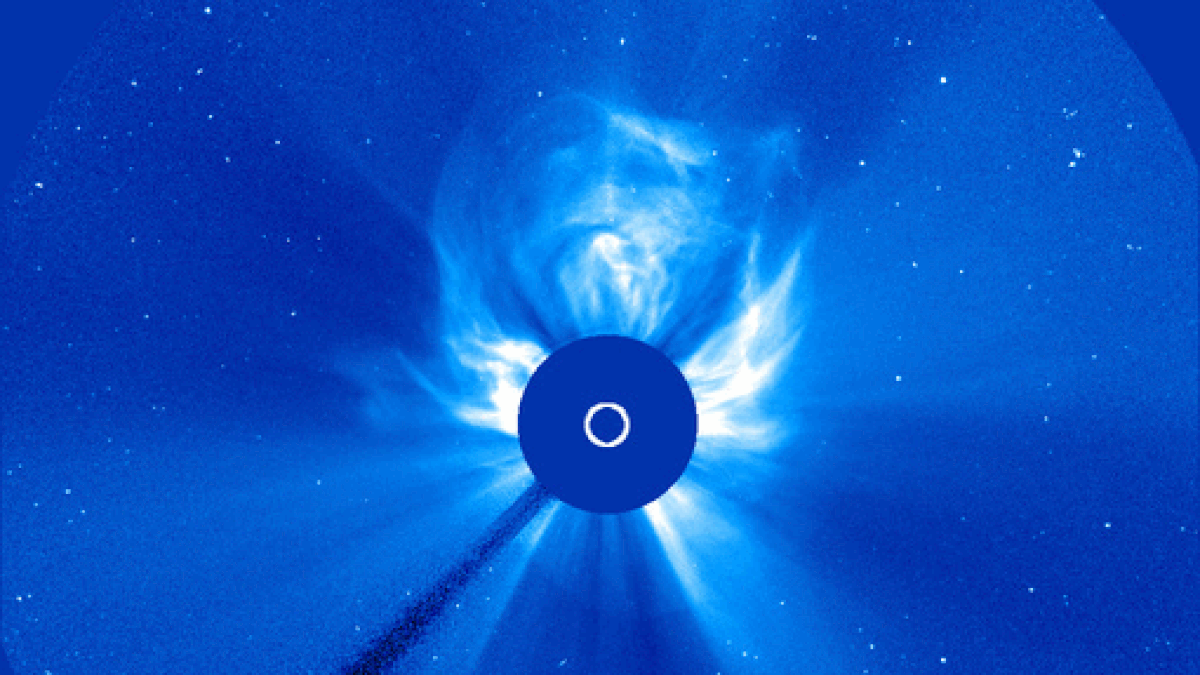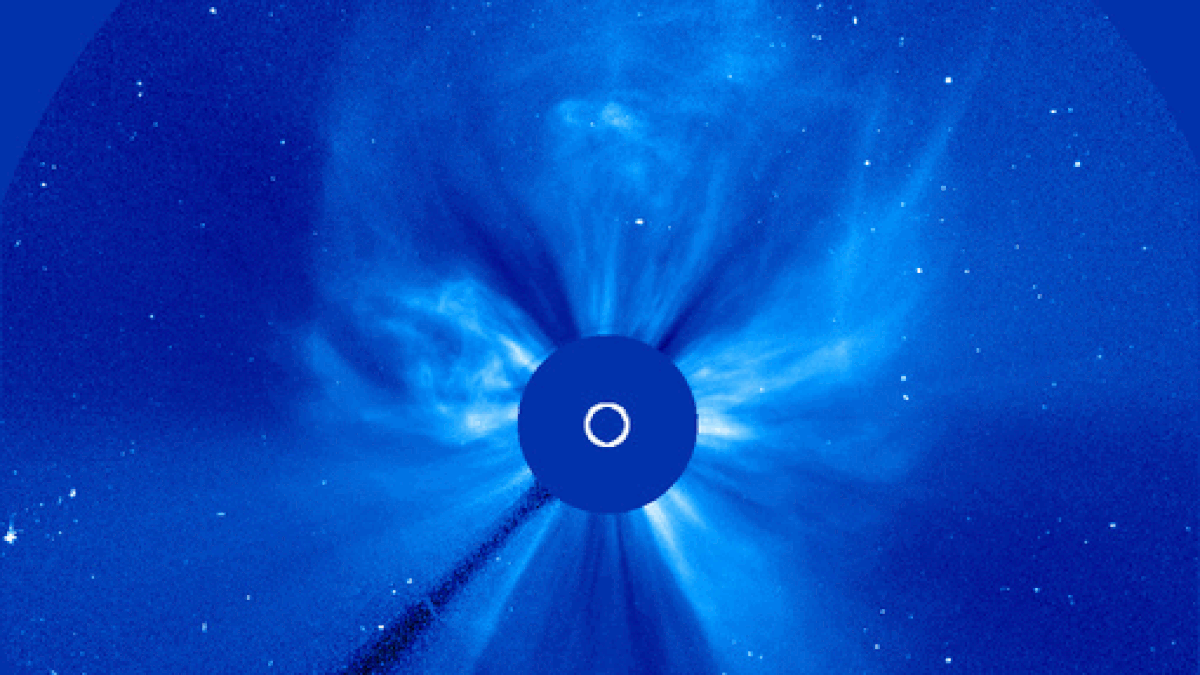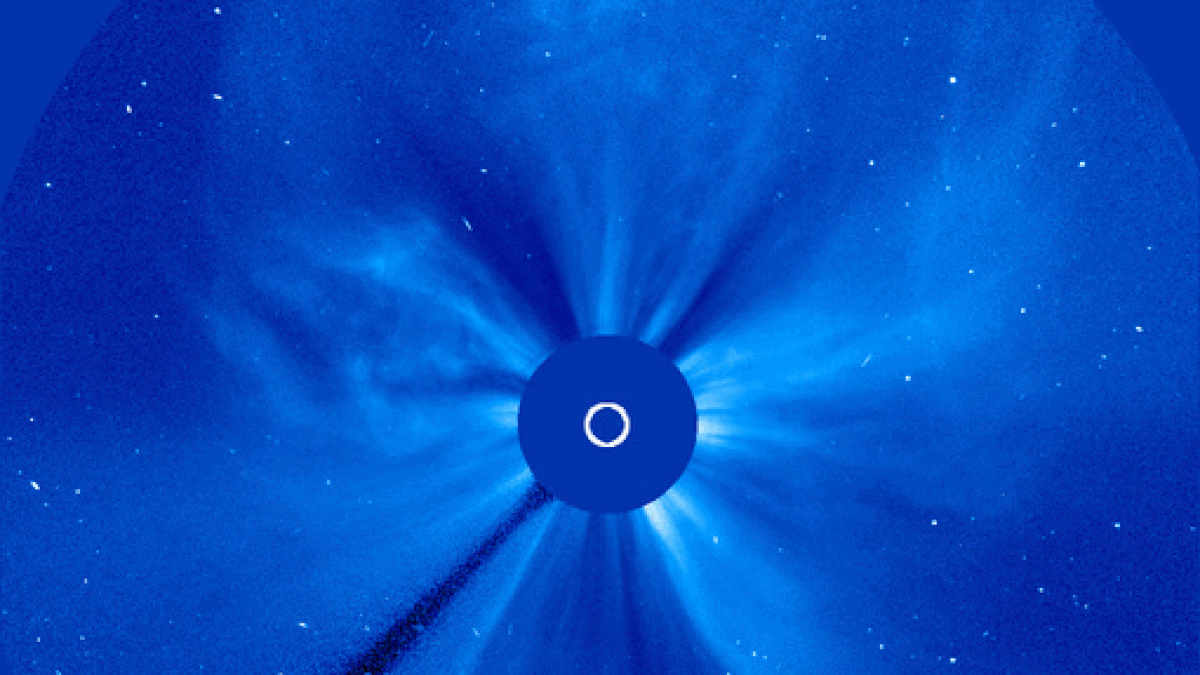
The surprising surge of photo voltaic exercise through the ongoing photo voltaic most could also be tied to a lesser-known, 100-year-long cycle that’s simply starting to ramp up once more, a brand new examine suggests.
If that is true, the following few many years might see additional will increase in photo voltaic exercise that will threaten Earth-orbiting spacecraft and proceed to set off vibrant auroras throughout the globe. Nevertheless, different specialists are skeptical of the brand new findings.
Photo voltaic exercise naturally waxes and wanes all through the photo voltaic cycle — a roughly 11-year interval wherein our dwelling star goes from being principally calm in a section referred to as photo voltaic minimal to being a chaotic mass that incessantly spits out highly effective photo voltaic storms at photo voltaic most, and again once more. This cycle is also referred to as the “sunspot cycle” as a result of the variety of darkish patches on the solar rises and falls resulting from adjustments within the solar’s magnetic subject, which utterly flips throughout photo voltaic most.
Nevertheless, there are a number of different cycles that dictate photo voltaic exercise. One instance is the Hale cycle, which governs how particular person magnetic bands transfer throughout the solar’s floor and has just lately been proven to affect the development of the sunspot cycle. Historic data additionally present that the solar has skilled a number of long-term fluctuations in photo voltaic exercise over the previous few millennia. These included the Maunder Minimal — a interval of enormously lowered photo voltaic exercise between 1645 and 1715.
One other, lesser-known repeating sample in photo voltaic exercise is the Centennial Gleissberg Cycle (CGC) — a variation within the depth of sunspot cycles that rises and falls each 80 to 100 years. The CGC remains to be poorly understood, however it’s probably tied to “delicate sloshing” of the magnetic fields in every of the solar’s two hemispheres that barely alters the Hale cycle, Scott McIntosh, a photo voltaic physicist on the newly fashioned house climate options firm Lynker House, who was not concerned within the analysis, advised Dwell Science.
Associated: 10 supercharged photo voltaic storms that blew us away in 2024
Within the new examine, printed March 2 within the journal House Climate, researchers recommend that the CGC might need simply “turned over,” or began once more. This might additionally clarify why the continued photo voltaic most, which formally started in early 2024, has ended up being a lot more durable to foretell than initially anticipated.
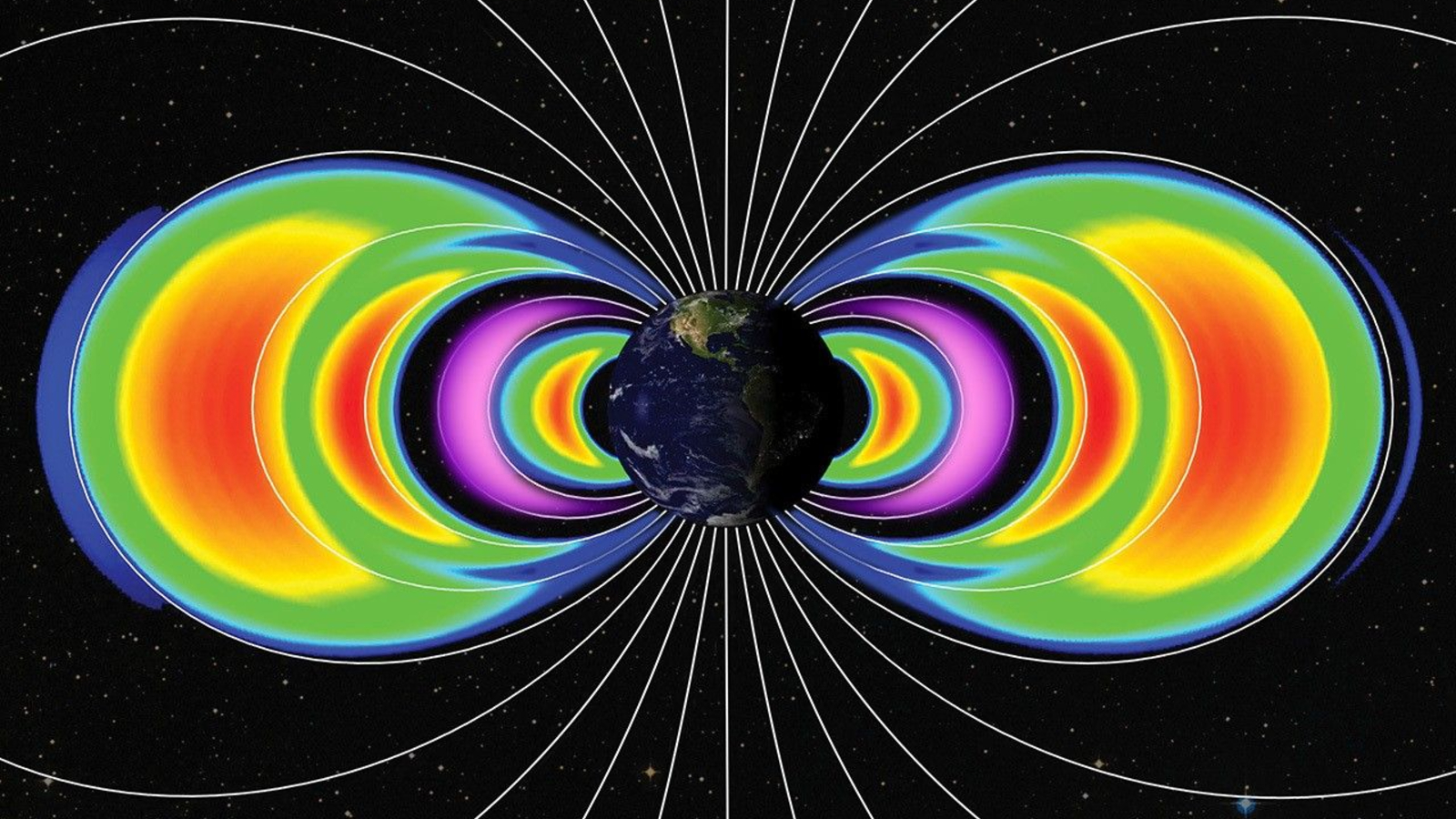
The examine workforce got here to this conclusion after analyzing adjustments to the “proton flux,” or variety of positively charged particles, in Earth’s interior radiation belt — the primary of two doughnut-shaped bands of charged particles surrounding our planet. Collectively, these bands are referred to as the Van Allen belts.
The interior belt’s proton flux decreases when photo voltaic exercise will increase due to interactions with Earth’s higher ambiance, which swells because it soaks up extra photo voltaic radiation. On the flip facet, the proton flux will increase as photo voltaic exercise decreases.
The brand new evaluation exhibits that the flux elevated over the previous 20 years however has simply began reducing over the previous 12 months or so. This implies that we’ve got “simply handed the CGC minimal” and that common photo voltaic exercise will begin to rise once more, examine lead writer Kalvyn Adams, an undergraduate researcher at JILA, a joint institute of the College of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder) and the Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Expertise, advised Dwell Science.
The proton flux knowledge had been collected by Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) satellites as they handed via the South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA) — a mysterious dent in Earth’s magnetic subject above South America and the South Atlantic Ocean the place our planet’s protecting protect is the weakest. This was a key cause these traits turned obvious, the researchers stated.
“The SAA is a area the place the Earth’s magnetic subject is weak and permits trapped protons to achieve decrease altitudes,” Adams stated. This enables the NOAA spacecraft to “see into” the interior radiation belt with out having to fly straight into it, which might be extraordinarily tough, he added.
Stunning photo voltaic exercise
We could also be nearing the tip of the utmost section of the present sunspot cycle, Photo voltaic Cycle 25 (SC25). This peak has been very energetic and has included some excessive house climate occasions, akin to a supercharged geomagnetic storm in Might 2024 that triggered among the most widespread auroras up to now 500 years. Nevertheless, this flourish of exercise was not initially anticipated.
Through the earlier sunspot cycle, SC24, the solar was surprisingly quiet all through photo voltaic most. This led house climate specialists from NASA and NOAA to initially forecast that the identical would occur throughout SC25, which they later admitted was a mistake.
The brand new analysis hints that SC24’s lull was attributable to the CGC minimal, probably making it the quietest sunspot cycle for round a century. If so, then the surprising exercise of the present photo voltaic most means the solar is returning to “enterprise as common,” McIntosh stated.
Earlier analysis had already recommended that the CGC could have performed a task within the latest sunspot cycle confusion, together with a 2023 examine from members of Adam’s analysis group and a 2024 paper that analyzed sunspot patterns with machine studying. Nevertheless, the latest findings are the primary to recommend that the CGC minimal could also be over.
The brand new examine additionally means that the CGC could have a higher affect on the sunspot cycle than researchers beforehand realized, Adams stated. Consequently, photo voltaic cycle forecasters ought to “positively” hold a better eye on this phenomenon when predicting upcoming cycles, he added.
Extra to come back?
If the CGC is popping over, then upcoming sunspot cycles will probably be as energetic as the present cycle and will ultimately get stronger as we strategy the CGC most, the researchers wrote.
“We simply handed the CGC minimal, and it will likely be one other 40 to 50 years earlier than the CGC most,” Adams advised Dwell Science. “Consequently, the following CGC most will probably happen round Photo voltaic Cycle 28.”
Utilizing “back-of-the-envelope calculations,” we will assume that when this occurs, photo voltaic exercise might be round twice as excessive because it has been through the present most, Adams added. Nevertheless, it’s onerous to inform for certain, as a result of the CGC’s impact on photo voltaic exercise “is usually a little inconsistent,” he admitted.
Associated: 15 dazzling photos of the solar
If future photo voltaic maxima are extra energetic than the continued peak, it might spell hassle for satellites, which could be knocked out of orbit as Earth’s higher ambiance swells. A number of spacecraft have already fallen foul of this up to now few years. Nevertheless, the issue might worsen within the coming many years because of the fast growth of personal satellite tv for pc “megaconstellations” which may be ill-equipped to cope with radiation spikes.
“Most [private] satellites normally take note of a mannequin of the house local weather when they’re being made,” Adams stated. However they “will not be contemplating the long-term variations that we’re seeing.”
Elevated photo voltaic exercise may be an issue for astronauts, who’re susceptible to dangerous radiation capturing out of our dwelling star, Adams added. And there’ll probably be tons extra individuals in house within the coming many years resulting from upcoming missions to the moon and Mars, in addition to an enhance in non-public spaceflight.
An unsure future
However not everybody utterly agrees with the brand new findings.
McIntosh, who was one of many first researchers to accurately forecast SC25 when he beforehand labored on the Nationwide Middle for Atmospheric Analysis at CU Boulder, advised Dwell Science that it’s “too early” to make any agency conclusions in regards to the CGC.
The primary concern is that proton flux has solely gone down over the previous 12 months, so it might simply be a brief dip attributable to the pure variability of the solar, McIntosh stated. Consequently, the examine workforce most likely wants a pair extra years of knowledge for his or her outcomes “to be definitive,” he added.
There’s additionally no baseline knowledge for evaluating CGC cycles, since satellites have solely been capable of precisely monitor proton flux over the previous 30 to 40 years.
McIntosh additionally warned that the brand new examine might be overestimating the results of the CGC on the sunspot cycle, as a result of we nonetheless do not understand how the 2 cycles work together. At current, researchers are additionally struggling to agree on what the CGC is and the way we outline it, he added.
Nevertheless, whereas McIntosh doesn’t solely agree with the brand new examine, he did say it’s “intriguing” and “properly intentioned,” and that the findings might assist forecast the following sunspot cycle. Whereas the CGC stays mysterious, it’s probably “an intrinsic a part of the [sunspot cycle] puzzle,” he added.