Scientific Research & Exploration: Check Out the Globe Via Study Research and Innovation
Organic bits that select the seabed make certain carbon monoxide 2 continues to be safeguarded. However, natural gel-like products decrease this treatment. Such microscale systems play a vital feature in enhancing environment forecasts.
Scuba divers recognize with water snow, small pieces of dead algae and various other microorganisms that gradually sink to the base of the sea. In overall, the enormous buildup of natural bits down payments over 50 gigatons of carbon at the end of the seas every year.
This procedure plays a vital task for the atmosphere, as the carbon bound in the little bits remains on the sea floor covering for countless years before resurfacing in the type of carbon monoxide 2 As A Result, it is very important to acknowledge what occurs to these little bits throughout their descent.
A research study hall led by Roman Stocker is finding this subject. The ETH group operates at the joint of different methods, containing microbiology, physics, mathematics, microfluidics, and oceanography.
In a research launched in the journal Nature Communications , the scientists reveal for the very first time that all-natural biogels significantly reduced the sinking rate.
The faster the loss, the less carbon monoxide gas 2 tires
“The rate at which the bits sink figures out just how much carbon is kept in the sea,” reviews Stocker. This is due to the fact that aquatic snow functions as a food source for bacteria as it gradually boils down to the sea floor covering.
All the carbon that is metabolized while doing so quickly winds up back in the environment as carbon monoxide gas 2 According to existing estimates, nearly 1 % of the sinking biomass gets to the seabed.
Till recently, scientists assumed water snow sank at rates in between 10 and 100 meters daily. Nonetheless Stocker’s team has presently situated proof that some little bits may boil down also slower.
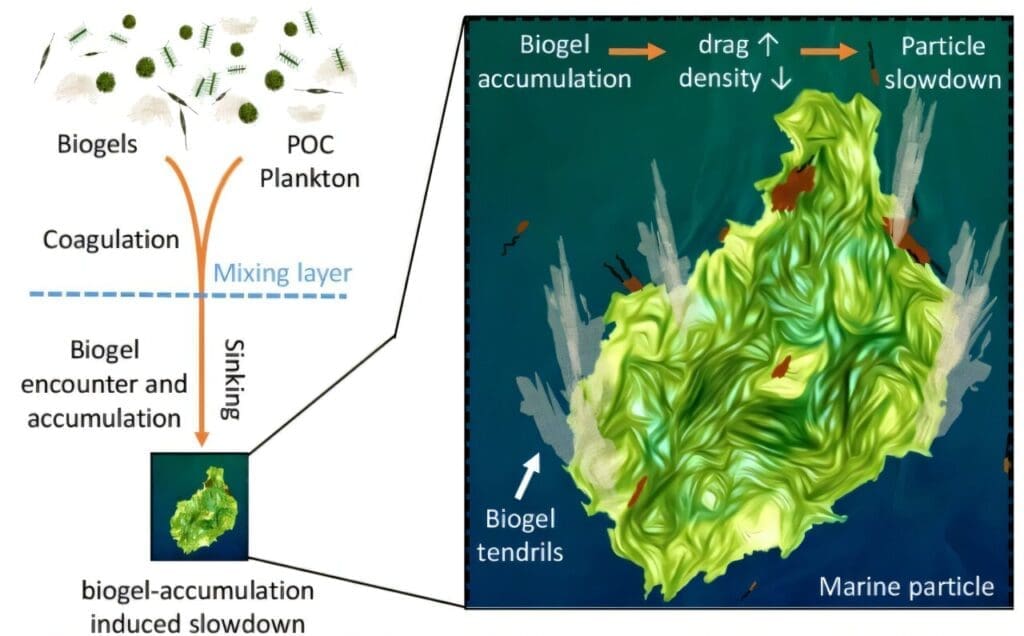
Biogels– clear, gelatinlike products produced by bacteria, algae and various other living microorganisms– supervise of this. These gels have various functions, from safeguarding microorganisms versus killers to capturing food, and typically drift in considerable quantities using the sea.
One research study in the Atlantic near Bermuda, for instance, discovered as much as 2 billion biogel bits per litre of seawater. Stocker’s team recommended that these gels happen bound with natural bits, minimizing their dropping price.
Tracking a little bit for days
A solitary piece can not be tracked outdoors sea over numerous days. This is why postdoctoral scientist Uria Alcolombri, currently an instructor at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, has in fact developed an unique product of research laboratory devices: a 20 -centimeter-high glass column loaded with salt water, having a solitary little bit postponed in between.
A counter-rotating water circulation changes the piece’s sinking, assuring it remains in the very same area. The rate of the counterflow stands for the sink rate.
The researchers used this to duplicate the sinking of a solitary piece for various days, both with biogel and without it. Aggregated pieces of the treatment of diatoms worked as the little bits. The group developed the biogel themselves making use of a water bacteria.
As anticipated, the gel-like product reduced the little bit’s descent. It truly reduced it far more than anticipated. In the presence of biogel, the little bits depended on the ground virtually 50 % a lot more gradually.
“We were impressed at simply exactly how big the outcome was,” mentions Stocker. This suggests that the a lot more biogel there is, the much less carbon gets to the seabed because bacteria have even more time to metabolize the carbon.
This stopping effect stems from the minimized thickness of biogels. When knotted with all-natural bits, the gel mimics a buoy, lowering their sinking rate. It in addition broadens like a parachute and kinds filamentous strings, which increase drag and far better decrease the motion. The team confirmed these attributes with a mathematical design.
“We anticipate these procedures to happen furthermore in the sea,” mentions Stocker. Nonetheless, there will definitely be significant abnormality outdoors seas. Various bacteria in different water locations produce varying amounts of biogel, which additionally differ in makeup. “We are attempting to expect this much far better with our mathematical layouts.”
According to Stocker, it makes good sense to gradually incorporate such systems right into atmosphere estimate variations. “There are a lot more treatments comparable to this that occur on a truly little range.” A few of them might additionally have the contrary effect, nevertheless much inadequate is comprehended concerning this.
“We need to open this black box and uncover completely particularly what is happening in the sea at the microscale.”
A lot more details: Uria Alcolombri et alia, Biogel scavenging lowers the sinking of natural pieces to the sea middles, Nature Communications (2025 DOI: 10 1038/ s 41467 – 025 – 57982 – 5
Offered by
Swiss National Scientific Study Structure
Citation :.
Why slower-sinking microorganisms are mischievous details for the atmosphere (2025, May 28.
brought 28 May 2025 from https://phys.org/news/ 2025 – 05 -slower-microorganisms-bad-news-climate. html.
This documents undertakes copyright. In addition to any kind of type of reasonable dealing for the objective of exclusive research or research study, no.
part might be reproduced without the made up permission. The product is taken care of details goals just.
Testimonial the full write-up from the first resource
.